Probiotics for Cancer: Akkermansia muciniphila and Clostridium butyricum Benefits, Evidence, and Supplement Strategies
Probiotics and Cancer: How Akkermansia muciniphila and Clostridium butyricum Can Support Treatment
Introduction
Your gut microbiome, the community of bacteria living in your digestive tract, plays a key role in your health, especially in fighting diseases like cancer. Akkermansia muciniphila and Clostridium butyricum are two probiotic bacteria showing promising benefits for cancer prevention and treatment support. This article explains simply how these probiotics can help and explores practical ways to include them in your health routine. Check out our specially formulated probiotic product here to conveniently include these beneficial bacteria in your daily regimen.
What is Akkermansia muciniphila?
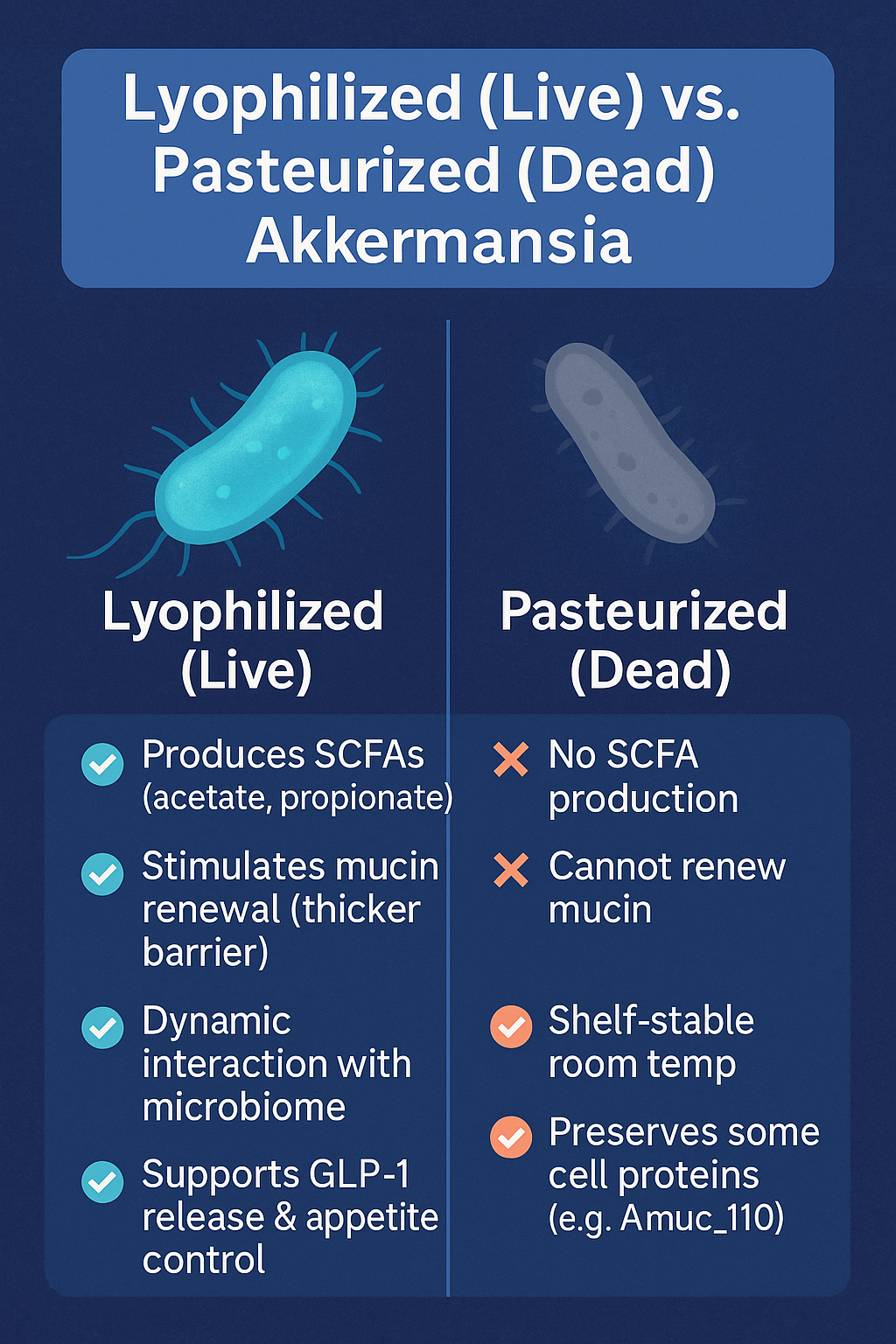
Akkermansia muciniphila is a beneficial gut bacterium known for protecting your digestive tract by strengthening the gut lining. It helps reduce inflammation and improves metabolic health, both crucial factors in reducing cancer risks.
Akkermansia and Cancer Prevention
Akkermansia muciniphila may lower cancer risk by:
-
Enhancing Gut Health:
Strengthens your gut barrier to prevent harmful substances from causing inflammation, a significant factor linked to cancer. -
Immune System Regulation:
Reduces chronic inflammation, thereby lowering cancer risk. -
Improving Metabolism:
Reduces obesity and insulin resistance, which are linked to cancer development.
Evidence of Akkermansia’s Benefits
Scientific research supports the beneficial role of Akkermansia:
-
Akkermansia improves the effectiveness of immunotherapy, especially in skin and lung cancers [Routy et al., 2018].
-
It helps manage chemotherapy side effects, improving patient comfort during cancer treatment.
What is Clostridium butyricum?
Clostridium butyricum is a helpful bacterium that produces butyrate, essential for gut health and protection against cancer.
Clostridium butyricum's Anti-Cancer Benefits
Clostridium butyricum helps fight cancer through:
-
Butyrate Production:
Butyrate feeds gut cells, eliminates cancer cells, and reduces inflammation. -
Supporting Immune Health:
Keeps the immune system balanced to prevent long-term inflammation linked to cancer. -
Epigenetic Influence:
Changes gene activity to slow or halt tumor growth.
Evidence Supporting Clostridium butyricum
Research confirms the benefits of Clostridium butyricum:
-
Higher levels of butyrate-producing bacteria are associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer [Louis et al., 2014].
-
Clostridium butyricum supplementation can improve gut health and reduce chemotherapy side effects.
Combined Power of Akkermansia and Clostridium
Taking Akkermansia muciniphila and Clostridium butyricum together may enhance their benefits by:
-
Boosting Immune Responses: Improving immune reactions during cancer treatment.
-
Enhanced Gut Protection: Protecting the gut lining during chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
-
Improved Metabolic Health: Reducing risks of obesity and diabetes linked to cancer.
Practical Probiotic Strategies for Cancer Support
Probiotics containing Akkermansia muciniphila and Clostridium butyricum can effectively support cancer treatments:
How to Take Probiotics Effectively
-
Supplements: Capsules or chewable tablets formulated to reach the gut alive.
-
Dietary Approaches: Foods rich in fiber and prebiotics to naturally boost probiotic populations.
Incorporating Probiotics with Cancer Treatments
-
Personalized Probiotics: Analyzing individual microbiomes for tailored probiotic choices.
-
Combined Therapy: Using probiotics to enhance the effectiveness and reduce the side effects of chemotherapy and immunotherapy.
Further Research Directions
Continued research is essential for:
-
Conducting extensive clinical trials to ensure safety and effectiveness.
-
Understanding how these probiotics interact at the molecular level with cancer treatments.
-
Developing clear guidelines for safely integrating probiotics into standard cancer care.
Conclusion
Akkermansia muciniphila and Clostridium butyricum offer significant potential for enhancing cancer prevention and treatment. Incorporating these probiotics into cancer care routines could improve outcomes, minimize side effects, and enhance overall quality of life.
By understanding these beneficial probiotics, you can better leverage their potential to combat cancer and promote overall health.
References
-
Routy, B., Le Chatelier, E., Derosa, L., et al. (2018). Gut microbiome influences efficacy of PD-1–based immunotherapy against epithelial tumors. Science, 359(6371), 91-97.
-
Louis, P., Hold, G. L., & Flint, H. J. (2014). The gut microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 12(10), 661-672.
.