Longevity and the Microbiota: How Gut Health Influences Lifespan
Introduction
Exploring the relationship between gut microbiota and longevity has become a cornerstone of modern health science. Exciting research reveals that the trillions of beneficial microorganisms living in our gut have a significant influence on our health, metabolism, immune response, and even cognitive functions. By nurturing a balanced gut microbiome, we can naturally support healthy aging, optimize our longevity, and enhance our quality of life (Claesson et al., 2012). Discovering how gut health impacts lifespan offers promising strategies for achieving vibrant health at any age.
What is Gut Microbiota?
The gut microbiota comprises the diverse community of beneficial microbes that reside in our digestive system. With approximately 100 trillion microbes representing up to 1,000 species, these organisms play vital roles, including aiding digestion, synthesizing vitamins, defending against pathogens, and regulating the immune system (Marchesi et al., 2016). Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is essential for longevity and overall wellness.
Gut Microbiota and Healthy Aging
As we age, our gut microbiota naturally shifts, often decreasing in diversity and increasing in pathogenic microbes, which contribute to inflammation and reduced immune function, a phenomenon known as inflammaging. However, studies suggest we can actively influence these changes positively by enriching our microbiome with beneficial bacteria like Akkermansia muciniphila, Lactobacillus, and Bifidobacterium. Supporting gut microbiota diversity through diet, probiotics, and lifestyle can effectively reduce inflammaging, enhancing healthspan and lifespan (O’Toole & Jeffery, 2015).
The Secret of Centenarians: Gut Microbiota and Longevity
Research into centenarians—individuals living over 100 years—provides invaluable insights into gut microbiota-driven longevity. Centenarians typically possess microbiomes abundant in beneficial bacteria, including Akkermansia, Christensenellaceae, and Bifidobacterium. These microorganisms help reduce inflammation, improve metabolic efficiency, boost immune function, and maintain gut barrier integrity (Biagi et al., 2016). Leveraging this knowledge, we can optimize our own microbiota to naturally promote longevity.
Akkermansia muciniphila: Key to Longevity
Akkermansia muciniphila is increasingly recognized as a pivotal bacterium supporting longevity. By thriving in the gut mucus layer, Akkermansia strengthens intestinal barrier function, reduces inflammation, regulates metabolism, and protects against obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases (Everard et al., 2013). Incorporating Akkermansia probiotic supplements into your daily routine can significantly enhance gut health, naturally supporting longevity and overall wellness.
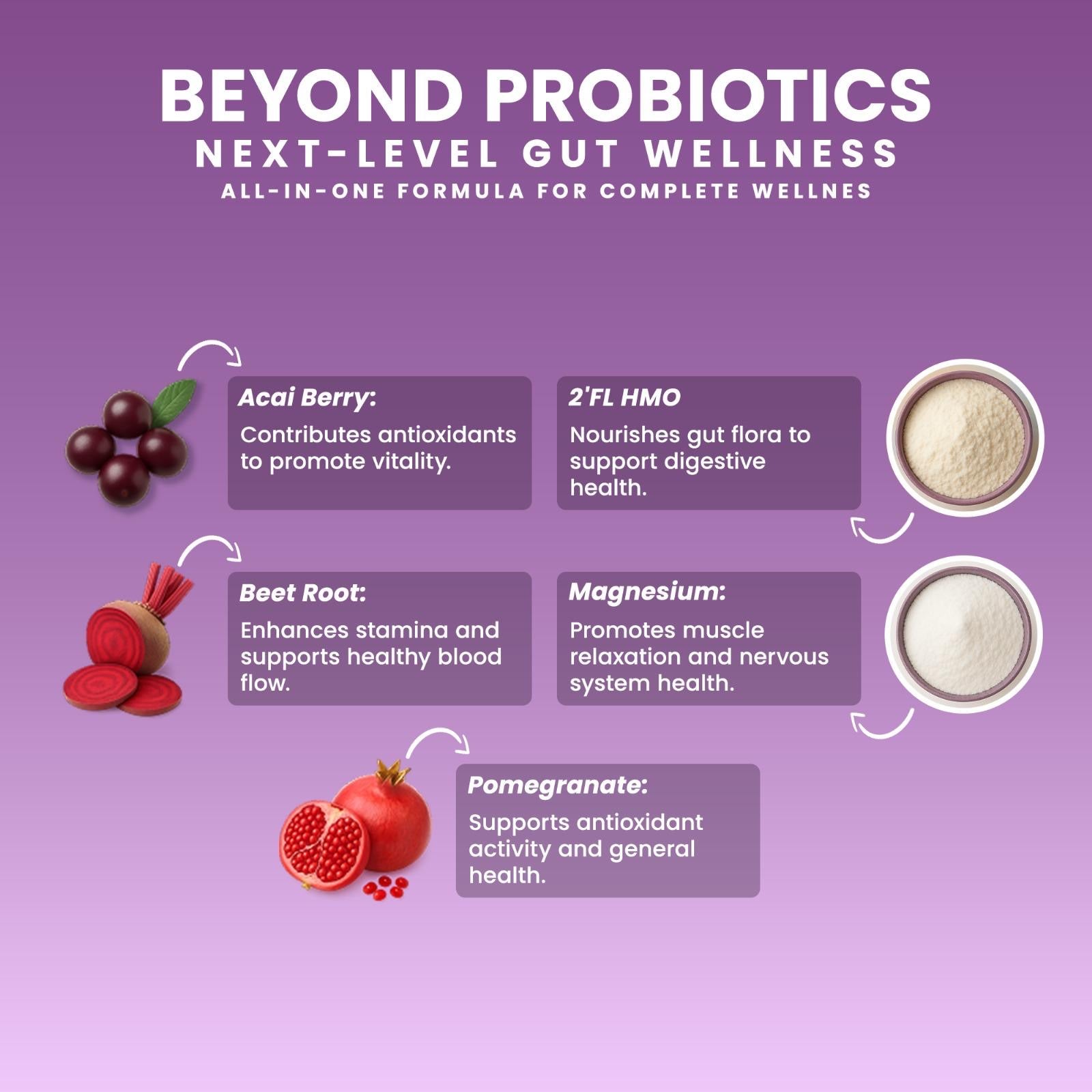
Probiotics and Prebiotics: Natural Boosters of Longevity
Using probiotics (beneficial microbes) and prebiotics (fibers that nourish beneficial microbes) strategically enhances gut microbiota health. Regularly consuming probiotics and prebiotic-rich foods—such as garlic, onions, bananas, and chicory root—improves microbial diversity, strengthens gut barriers, reduces inflammation, and enhances immunity, contributing to healthy aging (Hill et al., 2014). These dietary additions represent effective natural strategies for longevity.
Dietary Influence: Gut Health and Longevity
Your diet has a significant influence on gut microbiota composition, which in turn affects longevity. Adopting a microbiota-friendly diet rich in plant-based foods, fiber, and fermented products—like the Mediterranean diet—promotes microbial diversity, reduces inflammation, and supports healthier aging (De Filippis et al., 2016). Embracing dietary habits that favor gut health can naturally enhance longevity and overall wellness.
Intermittent Fasting and Longevity
Intermittent fasting and caloric restriction have a positive impact on gut microbiota by promoting beneficial bacteria, reducing inflammation, enhancing gut integrity, and increasing the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as butyrate and propionate. These SCFAs improve metabolic health, reduce inflammation, and promote longevity (Cani & Van Hul, 2020). Practicing intermittent fasting as part of your lifestyle can naturally boost gut health and longevity.
Exercise: Enhancing Longevity through Gut Health
Regular physical activity has beneficial effects on gut microbiota, enhancing microbial diversity, metabolic health, and immune function. Exercise reduces inflammation and positively influences microbial populations, supporting improved longevity and healthspan naturally (Mailing et al., 2019). Engaging in consistent exercise is a practical strategy to naturally optimize gut health for longevity.
Gut-Brain Axis: Cognitive Longevity through Microbiota
The gut-brain axis illustrates the critical connection between gut microbiota and cognitive health. Balanced gut microbiota supports cognitive function by reducing neuroinflammation and protecting against cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases (Cryan et al., 2020). Optimizing your gut microbiota can thus naturally enhance cognitive health, promoting longevity and a higher quality of life.
Conclusion
The powerful relationship between gut microbiota and longevity presents an inspiring and practical roadmap for achieving healthier aging naturally. By actively nurturing our microbiome through diet, probiotics, intermittent fasting, exercise, and stress management, we can positively influence inflammation, immunity, metabolism, and cognitive function. These microbiota-friendly practices offer tangible, hopeful pathways towards a longer, healthier, and more fulfilling life (Dinan & Cryan, 2017).
Further Reading: